Simplifying Communication with Spring Boot and ActiveMQ Queues and Topics
- pranaypourkar
- May 7, 2023
- 5 min read
Updated: May 22, 2023
Apache ActiveMQ is an open-source message broker that implements the Java Message Service (JMS) and the Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) protocol. It provides scalable, reliable, and high-performance message queuing and publish-subscribe messaging systems. ActiveMQ allows communication between applications by sending and receiving messages. It supports various messaging patterns such as point-to-point, publish-subscribe, request-reply, and others.
Let's discuss 2 commonly used messaging patterns in detail.
Point-to-Point (P2P): It is commonly referred to as queue-based messaging. In a P2P messaging model, messages are sent to and received from specific queues. Each message is typically consumed by only one receiver (or "consumer") from the queue, creating a one-to-one relationship between the sender and receiver.P2P messaging is useful when you need to send a message to a specific consumer or if you need to guarantee that a message is consumed only once.
Publish-Subscribe (Pub-Sub): In this case, messages are sent to a topic, and any number of consumers, which subscribes to this topic, can receive the message. In Pub-Sub messaging, a producer sends a message to a topic or a channel, and multiple consumers can consume that message. The producer does not know which consumer is going to consume the message, and the consumers don't know who is producing the message. Pub-Sub messaging is useful when you need to send a message to multiple consumers or if you want to create a broadcast-like messaging system.
For more details on ActiveMQ, visit the official website - https://activemq.apache.org/
Let's us proceed with setting up of ActiveMQ using docker-compose method.
docker-compose.yaml
version: "3.9"
# https://docs.docker.com/compose/compose-file/
services:
# ActiveMQ web url - http://localhost:8161/admin
activemq:
container_name: activemq
image: rmohr/activemq:5.15.4
ports:
- "61616:61616"
- "8161:8161"
environment:
ACTIVEMQ_ADMIN_LOGIN: admin
ACTIVEMQ_ADMIN_PASSWORD: admin
networks:
default:
name: company_defaultRun the docker-compose file to start the ActiveMQ service
docker-compose upActiveMQ console url
http://localhost:8161/admin
In this blog, we will create a Spring Boot application that sets up a queue and a topic in ActiveMQ based on the configuration provided in the application.yaml file. We will then implement separate producers that sends messages to the queue and the topic every 5 seconds. Additionally, we will create separate consumers for the queue and the topic.
Let's craft pom.xml file and add the required dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-activemq</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
</dependency>Let's look at application.yml file. Set the queue-name and topic-name as per need. Application will create the queue and topic with given name in ActiveMQ
server:
port: 4040
activemq:
broker-url: tcp://localhost:61616
queue-name: sample-queue
topic-name: sample-topicNow, we need to create a Config class which will establish connection with ActiveMQ, create queue and topic with given name and expose DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory and JmsTemplate spring beans with configuration for queue and topic. DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory bean will be used with @JmsListener annotation and JmsTemplate will be used to produce messages.
JmsConfig.java
package com.company.project.config;
import javax.jms.ConnectionFactory;
import javax.jms.Queue;
import javax.jms.Topic;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory;
import org.apache.activemq.command.ActiveMQQueue;
import org.apache.activemq.command.ActiveMQTopic;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jms.config.DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory;
import org.springframework.jms.core.JmsTemplate;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Configuration
public class JmsConfig {
@Value("${activemq.broker-url}")
private String brokerUrl;
@Value("${activemq.queue-name}")
private String queueName;
@Value("${activemq.topic-name}")
private String topicName;
@Bean
public ConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setBrokerURL(brokerUrl);
return connectionFactory;
}
@Bean
public DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory queueListenerFactory() {
DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory factory = new DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory();
factory.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory());
factory.setConcurrency("1");
factory.setPubSubDomain(false); // set pubSubDomain to false for queues
return factory;
}
@Bean
public DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory topicListenerFactory() {
DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory factory = new DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory();
factory.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory());
factory.setConcurrency("1");
factory.setPubSubDomain(true); // set pubSubDomain to true for topics
return factory;
}
@Bean
public Queue queue() {
return new ActiveMQQueue(queueName);
}
@Bean
public Topic topic() {
return new ActiveMQTopic(topicName);
}
@Bean
@Qualifier("queueJmsTemplate")
public JmsTemplate queueJmsTemplate() {
JmsTemplate template = new JmsTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory());
return template;
}
@Bean
@Qualifier("topicJmsTemplate")
public JmsTemplate topicJmsTemplate() {
JmsTemplate template = new JmsTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory());
template.setPubSubDomain(true);
return template;
}
}
It's time to create consumers for queue and topic.
ConsumerService.java
package com.company.project.service;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.jms.annotation.JmsListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class ConsumerService {
@JmsListener(destination = "${activemq.queue-name}", containerFactory = "queueListenerFactory")
public void handleQueueMessage(String message) {
log.info("Received message from queue: {}", message);
}
@JmsListener(destination = "${activemq.topic-name}", containerFactory = "topicListenerFactory")
public void handleTopicMessage(String message) {
log.info("Received message from topic: {}", message);
}
}Let's create a class with helpful methods to send and receive message
PubSubService.java
package com.company.project.service;
import javax.jms.Message;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.jms.core.JmsTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class PubSubService {
@Qualifier("topicJmsTemplate")
private final JmsTemplate topicJmsTemplate;
public void sendMessage(String topic, String message) {
topicJmsTemplate.convertAndSend(topic, message);
}
public Message receiveMessage(String topic) {
return topicJmsTemplate.receive(topic);
}
}QueueService.java
package com.company.project.service;
import javax.jms.Message;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.jms.core.JmsTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class QueueService {
@Qualifier("queueJmsTemplate")
private final JmsTemplate queueJmsTemplate;
public void sendMessage(String destination, String message) {
queueJmsTemplate.convertAndSend(destination, message);
}
public Message receiveMessage(String destination) {
return queueJmsTemplate.receive(destination);
}
}At last we will create producers which will produce message on the topic and queue every 4 seconds with the help of scheduler.
Note: We are using RandomStringUtils to generate random strings
MessageSchedulerService.java
package com.company.project.service;
import javax.jms.JMSException;
import javax.jms.Queue;
import javax.jms.Topic;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomStringUtils;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class MessageSchedulerService {
private final QueueService queueJmsTemplate;
private final PubSubService topicJmsTemplate;
private final Queue queue;
private final Topic topic;
// Sending every 4 seconds
@Scheduled(cron = "*/4 * * * * *")
public void sendQueueMessage() throws JMSException {
String randomString = RandomStringUtils.randomAlphabetic(5);
log.info("Sending string: {} to the queue: {}", randomString, queue.getQueueName());
queueJmsTemplate.sendMessage(queue.getQueueName(), randomString);
}
// Publishing every 4 seconds
@Scheduled(cron = "*/4 * * * * *")
public void sendTopicMessage() throws JMSException {
String randomString = RandomStringUtils.randomAlphabetic(5);
log.info("Publishing string: {} to the topic: {}", randomString, topic.getTopicName());
topicJmsTemplate.sendMessage(topic.getTopicName(), randomString);
}
}Finally, we will build our application and run to see it in action.
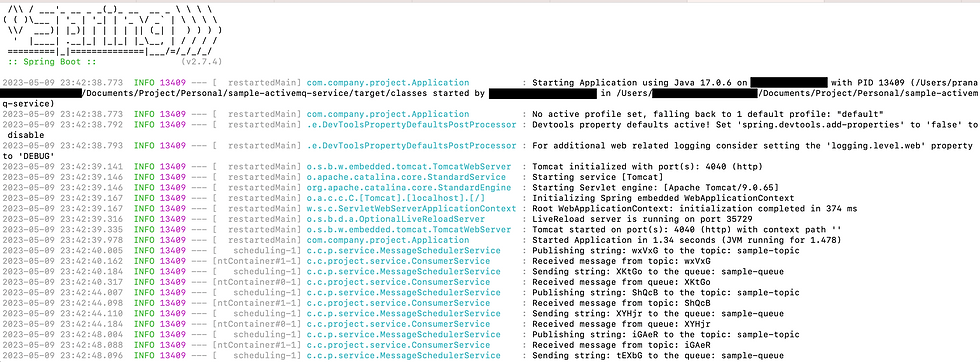
mvn clean install mvn spring-boot:runWe can verify from the logs that messages are getting produced and consumed from the queue and topic
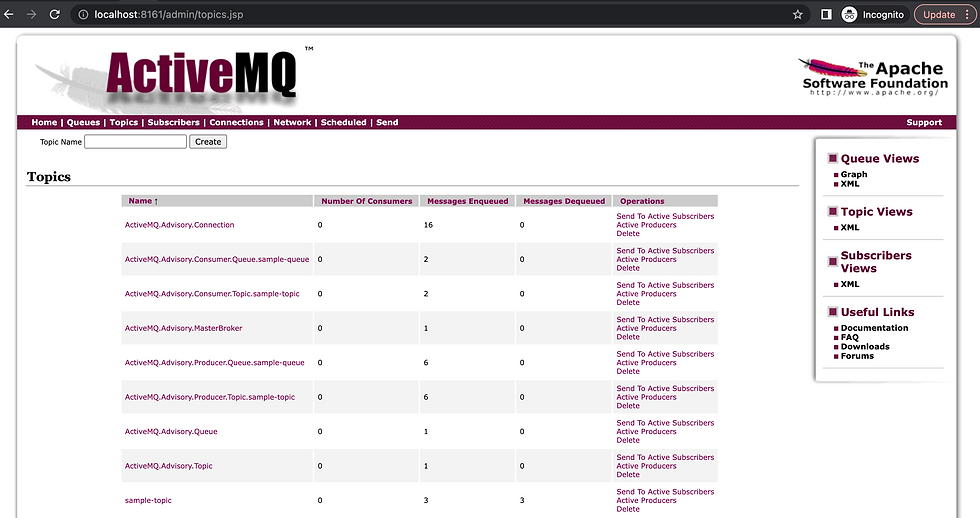
Let's verify from the ActiveMQ console as well.
Queues

Topics
ADDON Feature
We can create a controller with endpoints to produce and consume message from the queue and topic.
package com.company.project.controller;
import com.company.project.service.QueueService;
import com.company.project.service.PubSubService;
import javax.jms.JMSException;
import javax.jms.Message;
import javax.jms.Queue;
import javax.jms.TextMessage;
import javax.jms.Topic;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/messages")
public class MessageController {
private final QueueService queueService;
private final PubSubService pubSubService;
private final Queue queue;
private final Topic topic;
// Send message to the Queue
@PostMapping("/queue")
public ResponseEntity<?> sendToQueue(@RequestBody String message) throws JMSException {
queueService.sendMessage(queue.getQueueName(), message);
return ResponseEntity.ok().build();
}
// Receive message from the queue
@GetMapping("/queue")
public ResponseEntity<String> receiveFromQueue() throws JMSException {
Message message = queueService.receiveMessage(queue.getQueueName());
return ResponseEntity.ok(((TextMessage) message).getText());
}
// Send message to the topic
@PostMapping("/topic")
public ResponseEntity<?> sendToTopic(@RequestBody String message) throws JMSException {
pubSubService.sendMessage(topic.getTopicName(), message);
return ResponseEntity.ok().build();
}
// Receive message from the topic
@GetMapping("/topic")
public ResponseEntity<String> receiveFromTopic() throws JMSException {
Message message = pubSubService.receiveMessage(topic.getTopicName());
return ResponseEntity.ok(((TextMessage) message).getText());
}
}Files are attached for the reference below.
Thank you for taking the time to read this post. I hope that you found it informative and useful in your own development work.




Comments